How To Start A Smallholder Dairy Farm In Kenya: A Guide For Dairy Farming Success
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Benefits of Starting a Smallholder Dairy Farm
- Planning Your Dairy Farm
- Selecting and Managing Your Herd
- Milking and Milk Production
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Kenya’s dairy sub-sector has seen recent growth. This is because the demand for dairy produce and products is also rising too. More people, urbanization, and higher incomes drive the country’s dairy sub-sector on an upward trajectory. The dairy farming is vital for farming economies and it supports millions of people in the rural areas. Large commercial dairy farms are crucial for meeting milk production targets in the country. However, smallholder dairy farms are also important as they supply a large, over 80%, of the Kenya’s total milk volume. In this article we are going to explore more about dairy farming.

Benefits of Starting a Smallholder Dairy Farm
- Offers farmers and their families a steady income when managed well.
- It is rich in vital nutrients. These include protein, calcium, and vitamins. They improve health, food and nutrition security in many households.
- Promote self-sufficiency by reducing dependency on external sources for milk and dairy products.
- Creates employment opportunities.
- It allows farmers to add variety to their income. This reduces reliance on one source of money.
Planning Your Dairy Farm
Land & Location
Choosing suitable land is crucial for the success of your dairy farm. Consider the following factors when assessing land for dairy farming in Kenya:
- Water Availability: Ensure access to reliable sources. Adequate water availability is essential for maintaining herd health and supporting pasture growth.
- Test the soil to check its quality: The tests will look at its fertility and if it is suitable for pasture. Good soil has drainage and nutrients. It’s ideal for growing nutritious cattle fodder.
- Climate and Weather Patterns: Choose land that is good for dairy farming. It should minimize the risk of extreme weather.
- Accessibility: Good transportation infrastructure reduces logistical challenges and operating costs.
- Size and Topography: Choose land with gentle slopes. It should have minimal erosion risk. This will help pasture management and prevent soil degradation.
- Proximity to the market: Being close to cities or dairy processors can cut shipping costs. It can also improve your market access.
Business Plan
Creating a strong business plan is crucial for your dairy farm. It guides the strategy and ensures long-term success. Your business plan should include the following components:
- Goals and Objectives
- Budget and Financial Projections
- Target Market Analysis
- Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Risk Management Plan
Permits & Regulations
Before you start your dairy farm, know and follow the needed permits and rules. They cover dairy farming in Kenya. Consider the following steps:
- Research the rules. Learn the laws, regulations, and licensing requirements for dairy farming in Kenya. Consult government agencies such as the Kenya Dairy Board for guidance.
- Get the needed permits and licenses for starting a dairy farm. This includes land-use, environmental, and livestock movement permits.
- Comply with Health and Safety Standards. Ensure compliance with health and safety
- standards for dairy farming. This includes proper sanitation, animal welfare, and waste management. Stay informed. Attend workshops, seminars, or training programmes. These are offered by agricultural extension service providers or dairy value chain actors associations. They should cover best practices and compliance requirements.
Selecting and Managing Your Herd
Choosing the Right Breed
When selecting dairy cow breeds for Kenyan smallholder farms, consider the following factors:
- Adaptability to climate
- Milk production potential
- Disease resistance
- Feeding efficiency
- Breed Suitability for crossbreeding
Dairy cow breeds, Kenya, selection.
Building a Healthy Herd
Maintaining animal health is essential for the success of your dairy farm. Follow these guidelines to ensure a healthy herd:
- Provide a balanced diet. It should be rich in nutrients, such as energy, protein, vitamins, and minerals. This diet supports optimal maintenance, growth, reproduction, and milk production.
- Implement a comprehensive vaccination programme to protect your herd against common diseases
- Adopt good breeding strategies. They will improve your herd’s genes over time.
Housing and Management
- Provide clean, dry, and comfortable housing for your cows. This will ensure their health and well-being.
- Build strong, airy barns or sheds. They protect your cows from bad weather like rain, wind, and extreme temperatures. Use dry straw, sawdust, or sand for bedding. It gives cows a soft, dry resting surface.
- Set up strict hygiene rules to lower disease spread among animals.
- Ensure access to clean drinking water and nutritious feed at all times.
Milking and Milk Production
Milking Techniques
Good milking techniques are essential. They ensure animal welfare, keep milk quality high, and maximize milk production. Follow these guidelines for effective milking:
Step 1: Observation
Identify cows that must be milked last or are receiving treatment.
Step 2: Fore stripping
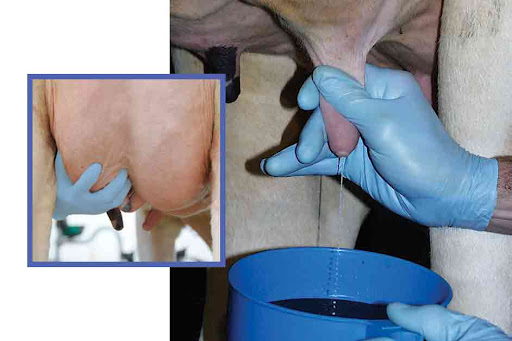
Flush out bacteria from the teat canal and stimulate milk flow. Use a strip cup for better detection of abnormal milk. Ensure that you forestrip all the quarters before all milking times. Examine by hand if milk is abnormal
Step 3: Cleaning the Teats
Use a disinfectant solution approved by the veterinarians. Ensure the pre-dip solution remains in contact with teats for at least 30 seconds. Only wet the teats an thoroughly wipe with a dry single-service towel. Pay attention to teat ends. Use alcohol swabs to test teat cleanliness
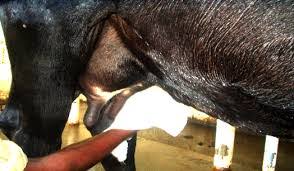
Step 8: Disinfection
Once milking is done, dip the teats fully in a disinfectant approved by veterinary professionals in the country. Teat dip cups must be clean. Discard any unused solution. Clean the container well. Prepare a fresh solution for each milking.
Milk Handling and Storage
Good milk is key for good dairy products. It gives taste and flavour. It is free from pathogens and has a good keeping quality. Good quality dairy products cannot and can never be made from poor quality raw milk. Good raw milk must be free from debris and sediments. It must be free from off-flavours and have low bacterial count. It must, also, have normal acidity and composition and be free of antibiotics and hazardous chemicals.
Proper Sanitation of :
- Milk Cans
- Cold Water Rinse: Immediately rinse milk cans with cold water after they are emptied of milk.
- Scrub the cans thoroughly with a brush and warm, unperfumed liquid soap.
- Cold Water Rinse for a second time: Rinse the cans again with cold water.
- Sterilization: Sterilize (sanitize) the cans by boiling water or steam, if available.
- Drying: Dry the cans on a drying rack. Exposure to sunlight during drip drying can enhance the killing of bacteria.
2. Cows
- Milking Hygiene: Follow proper milking hygiene practices.
- Milk mastitis cows last and discard their milk.
- Do not mix milk from cows treated with antibiotics with milk from healthy cows.
- Adhere to the required 4-day withdrawal period for milk from treated cows.
- Quality is important. Milk with antibiotics can harm consumers. It can also harm the quality of dairy products.
3. Milk Transport Vessels (Cans and Tanks)
- Cleaning: Clean all milk transport vessels, such as cans and tanks. Use the same procedures outlined for milk cans.
- Rinsing: Ensure milk cooling centers have water for rinsing milk transport vessels. The water must be cold.
Marketing Your Milk
You must understand local markets. You must identify potential ways to sell your milk. This is key for making the most money and reaching target consumers. Consider the following strategies for marketing your milk:
- Market research
- Direct sales
- Value-added products
- Challenges & sustainability
Financing and Budgeting
Getting financing and managing costs are key challenges. They are critical for small dairy farmers. Consider the following strategies for financing your dairy farm and maintaining financial sustainability:
- Find sources of start-up capital. These include personal savings and loans from financial institutions.
- Cost-Effective Infrastructure: Optimize capital expenditures by investing in cost-effective infrastructure and equipment.
- Make a full budget. It should list your expected expenses and revenue for each part of your dairy farm.
- Monitor cash flow often. Cut costs to reduce expenses and increase profits.
- Manage risk. Do this by diversifying income sources. Consider using risk management strategies. For example, use forward contracting for milk sales. Or, hedge against commodity price swings.
Labour & Manpower
Managing labour is crucial. It keeps your dairy farm efficient and productive. Consider the following strategies for planning labour needs and optimizing manpower solutions:
- Assess your labour needs based on your farm’s size, herd, and workload.
- Invest in training and skill programmes for your farm workers. These will improve their knowledge and skill. They are in dairy farming, animal care, and equipment use. Provide ongoing training opportunities to empower employees and promote continuous improvement.
- Use labour-saving techniques and machines to speed up farm operations. This will cut manual labor needs.
- Explore other labour options. This could mean hiring part-time or seasonal workers. You could also outsource non-core tasks.
Environmental Sustainability
Promoting sustainability is key. It ensures the long-term success of your dairy farm. Consider the following practices for environmentally responsible dairy farming and waste management:
- Conserve resources. Use methods like rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation, and efficient water use. These methods reduce waste and save natural resources.
- Nutrient Management: Develop plans to optimize fertilizer usage. They should minimize runoff and leaching from manure storage.
- Improve energy efficiency on your dairy farm. Do this by investing in efficient equipment and renewable energy. For example, solar panels or biogas digesters. Also, use energy conservation measures like LED lighting and insulation.
- Protect and enhance on-farm biodiversity. Do this by saving natural habitats, planting and native plants. These things help beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife.
- Develop waste management plans. Make them cover manure, wastewater, and other farm waste. The plans should reduce their adverse environmental impacts.
Conclusion
Starting a successful smallholder dairy farm in Kenya requires careful planning. It also needs dedication and a commitment to excellence. Here are key steps to ensure your dairy farm’s success. They are strategic planning, herd management, milking & milk production, and challenges & sustainability. Consider joining extension programmes. Attend workshops and seminars. Also, connect with industry experts and organizations that offer valuable insights and support.
A dairy farm brings income for you and your family. It also helps nutrition, food security, and rural development in Kenya. Keep nurturing your passion for dairy farming. Embrace innovation and best practices. Never stop learning and growing.

